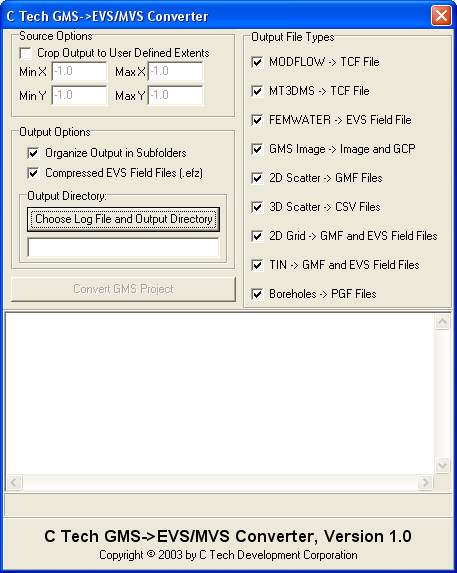
The GMS->EVS/MVS Converter takes as input a GMS project file (*.gpr) and parses it looking for parts that can be converted to an EVS/MVS file format. This supports all version 4 GMS projects only. To fully convert a MODFLOW, MT3DMS, or FEMWATER project make sure to run that simulation in GMS and save your project before attempting a conversion. There should only be one loaded solution for each model.
The following GMS Project and File types are convertible into their respective C Tech (EVS/MVS) file types:
MODFLOW: This converts into both EVS/MVS field files (*.eff, *.efz) and into an EVS/MVS TCF file (*.tcf) for animation.
MT3DMS: This converts into both EVS/MVS field files (*.eff, *.efz) and into an EVS/MVS TCF file (*.tcf) for animation.
FEMWATER: FEMWATER converts only into an EVS/MVS field file (*.eff, *.efz) at this time, because it is only handling steady state FEMWATER models. When this is rewritten to handle transient FEMWATER models, a TCF file (*.tcf) will also be added.
IMAGE: Image files (*.tif and *.jpg) are copied into the output directory and a georeferencing file (*.gcp) is created for image orientation.
2D SCATTER: These files are converted into EVS/MVS Geology Multi File format (*. gmf).
3D SCATTER: These files are converted into EVS/MVS 3D analyte (e.g. chemistry) files (*.apdv).
2D Grid: 2D Grid files are converted into the EVS/MVS Field file format (*. eff, *.efz) as well as EVS Geology Multi file format (*.gmf).
TIN: TIN files are converted into the EVS/MVS Field file format (*.eff, * .efz) as well as EVS Geology Multi file format (*.gmf).
BOREHOLE: BOREHOLE data is converted to the EVS Pre-Geology file format (*. pgf).
There is one source control option. By clicking on Crop Output to User Defined Extents the input from GMS can be focused on areas of interest to the user. These extents are assumed to be valid when entered by the user. No Error checking is done. This works only on MODFLOW, MT3DMS, and FEMWATER conversions.
There are two options for output:
Organize output to subfolders: This allows the user to keep track of which specific part of the project was converted by placing the appropriate converted files in new subfolders based on the data type (e.g. MODFLOW, IMAGE, etc.).
Compressed EVS Field Files(*.efz): This option changes all EVS/MVS field files (*.eff) into their compressed form (*.efz) for space saving purposes.
To run the converter
Select all appropriate options and file types to be converted.

Click the Choose Log File and Output Directory button to choose the destination for the log file and converted files/folders. The log file is a status report of the converter which keeps track of all errors and files created.
Next click on the Convert GMS Project button and select the GMS project file (*.gpr) to be converted. All files should be created and shown in the Status window, click Done to finish.
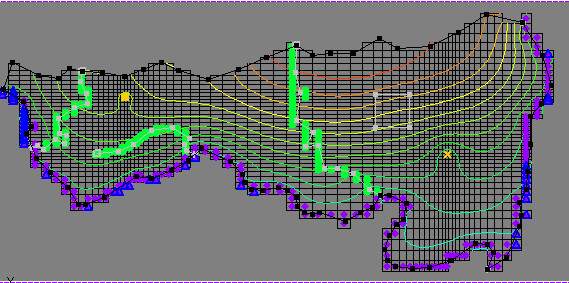
Example:
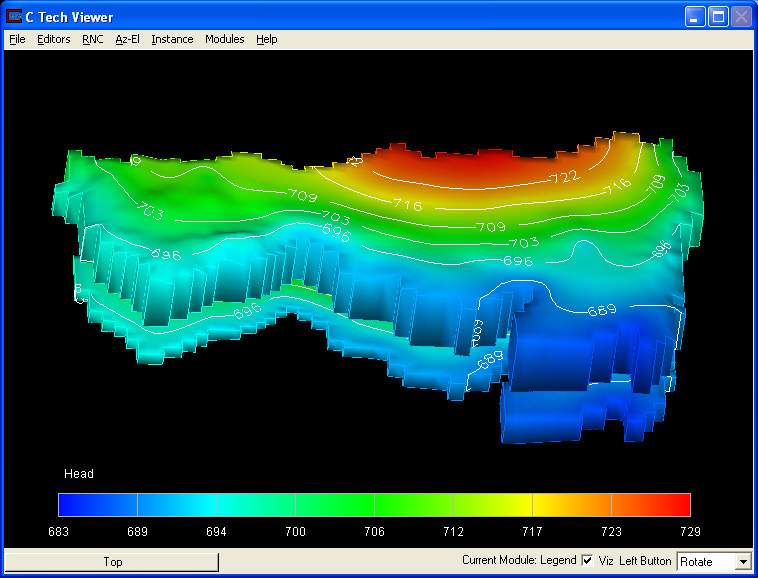
The following sample MODFLOW model in GMS was converted using the converter:
Upon running the GMS to EVS converter, a compressed EVS field file was created. This file can then be used in a variety of ways in EVS, as shown in the picture showing head values below:
© 1994-2018 ctech.com