plume_area is a module that allows us to subset the output of Krig_2D to include only those regions having nodal data values above (or below) a specified iso-level. It also allows us to select the specific scalar nodal data component we wish to use for coloring the graphical objects.
Locating modules
plume_area is the third module in the Subsetting library in the top section of the Network Editor.
Instance plume_area
Point to plume_area; then, holding down the left mouse button, drag plume_area into the Application window .

EVS doesn't care how we place modules in the Application window . But a good placement of modules results in cleaner looking connection lines, as we'll see in a later step. What you should note here is that plume_area in NOT in the network. The data flow is from Krig_2D to Viewer and is not passing through plume_area.
Modules List
The Modules List now shows Krig_2D, Viewer and plume_area:
However, you don't really ever need to use the Modules List, since you can open any module's user interface (Control Panel) by double clicking on that module.
Insert plume_area into the current network
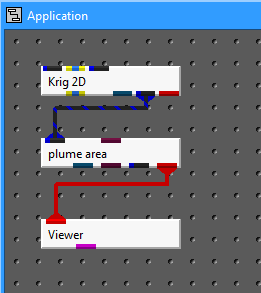
Let's now disconnect Krig_2D and Viewer and create a network from Krig_2D to plume_area to Viewer.
First, With the mouse, point to plume_area's leftmost input port (called input port 1). Next, connect the pointer to Krig_2D's blue-black output port. Now connect Viewer's input port to plume_area's second (red) output port, as shown in the diagram below.
What each connection means
Let's look briefly at what each connection means:
|
Connection |
Meaning |
|
plume_area to |
plume_area creates a subset of the output of Krig_2D. Krig_2D reads an EVS analyte (e.g. chemistry) file. Its third output port (blue-black) makes the data available as an EVS field. |
|
Viewer to plume_area |
Viewer defines a full-featured viewer. It renders the graphics-display objects passed to its input port. |
© 1994-2018 ctech.com